Paper Link –> Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning
Summary:
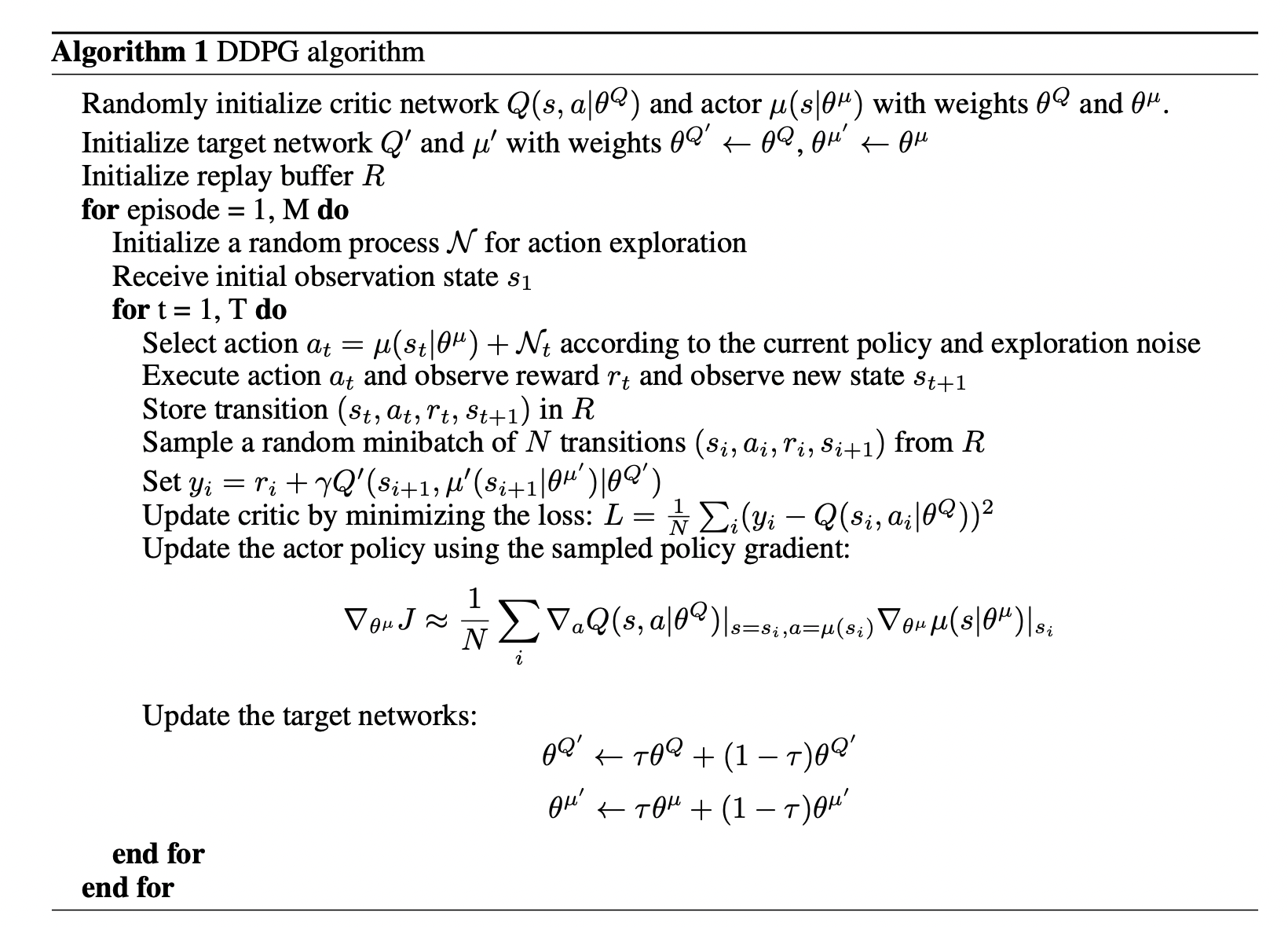
The author has proposed an algorithm designed to operate on continuous control, overcoming the limitations of the existing DQN approach, which is inadequate in continuous action spaces due to the dimensionality curse and discretion, which discards valuable information. This algorithm utilizes deep learning architecture operating on the actor-critic method in a model-free setting for a deterministic policy gradient.
Previous approaches relied on linear function approximators, which were only effective in low-dimensional problems. On top of that, they lacked scalability and suffered from unstable training, making them unsuitable for high-dimensional settings. The DDPG algorithm is inspired by the DQN approach and incorporates key features such as replay buffers and target networks to ensure stable learning.
DDPG exhibits superior performance in continuous control spaces by leveraging non-linear approximators such as neural networks, allowing for online learning and operation in continuous action spaces with stable training through replay buffer, target network and noise for exploration. Also, this paper shows that the DDPG was able to learn a good policy for the more complex task in spite of the overestimation or biases problem in Q-learning. Moreover, utilizing pixels alone has outperformed methods that rely on planners with full access to the dynamics and derivatives.
Strong Points:
- DDPG is an off-policy algorithm that utilizes experience replay, which allows the agent to learn from past experiences rather than relying solely on current experiences. Storing previous experiences in a replay buffer reduces the correlation between samples, leading to more efficient and stable learning.
- Utilizing a target Q network is a crucial aspect of the DDPG algorithm, contributing to divergence. Also, empirical evidence supports the significance of target networks, as they enhance stability and efficiency in the learning process.
- Using Batch Normalization to scale the state values for different environments. Also, state-of-the-art results are achieved on 20 physics simulation tasks without change in algorithm, network architecture, and hyper-parameters, exhibiting its robustness.
- Handling the exploration in continuous action spaces as random sampling will not work. Since it is also off-policy exploration is independent as a result, OU noise is added to the actor policy
Weak Points:
- Since in Mujoco environment feedback is provided at every step, which is the case in most real applications, this approach might fail as it depends only on the extrinsic reward.
- Also, the assumption is made as fully observable. Though it performed well in the existing environment, making it work in a partially observable setting would be challenging.
Reflections:
- A promising avenue for improving sample efficiency and performance gains in machine learning tasks is using self-supervised learning approaches for learning better representations.
This page was last updated at 2024-12-21 01:09.